Powering the Last Mile: Solar-based, Equitable Charging Infrastructure for Electric Thre Wheelers in West Bengal, India
Ahana Mukherjee, Electrical & Computer Engineering
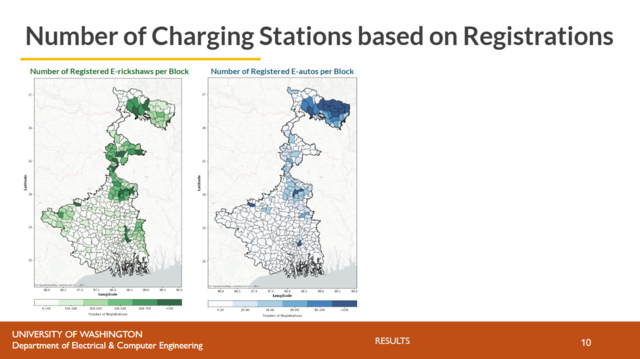
Electric three wheeler vehicles serve as a crucial bridge between private and public mobility modes by providing first- and last-mile connectivity. These vehicles are particularly common in India due to their demand responsive and cost-competitive nature in the public transport sector and serve as one of the country's early adopters of electric vehicle technologies. This study assesses the techno-economic feasibility of implementing photovoltaic-based, grid-independent, and spatially equitable charging infrastructure for electric three wheelers in West Bengal, India. Through a combination of technical sizing of battery charging systems, energy economics, and geospatial analysis of socio-economic indicators such as population size, relative wealth index, distances to public transport nodes, and population-based modes of travel and commuting (e.g. via on foot and bus), the study proposes priority locations for siting charging infrastructure based on the current electric three wheeler demand. This presentation will elaborate on the data analysis of the aforementioned socio-economic variables to ensure equitable spatial distribution of charging infrastructure intended to serve lower-income populations while enhancing the last-mile services of electric three wheelers.